What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of

PPT DNA Fingerprinting PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
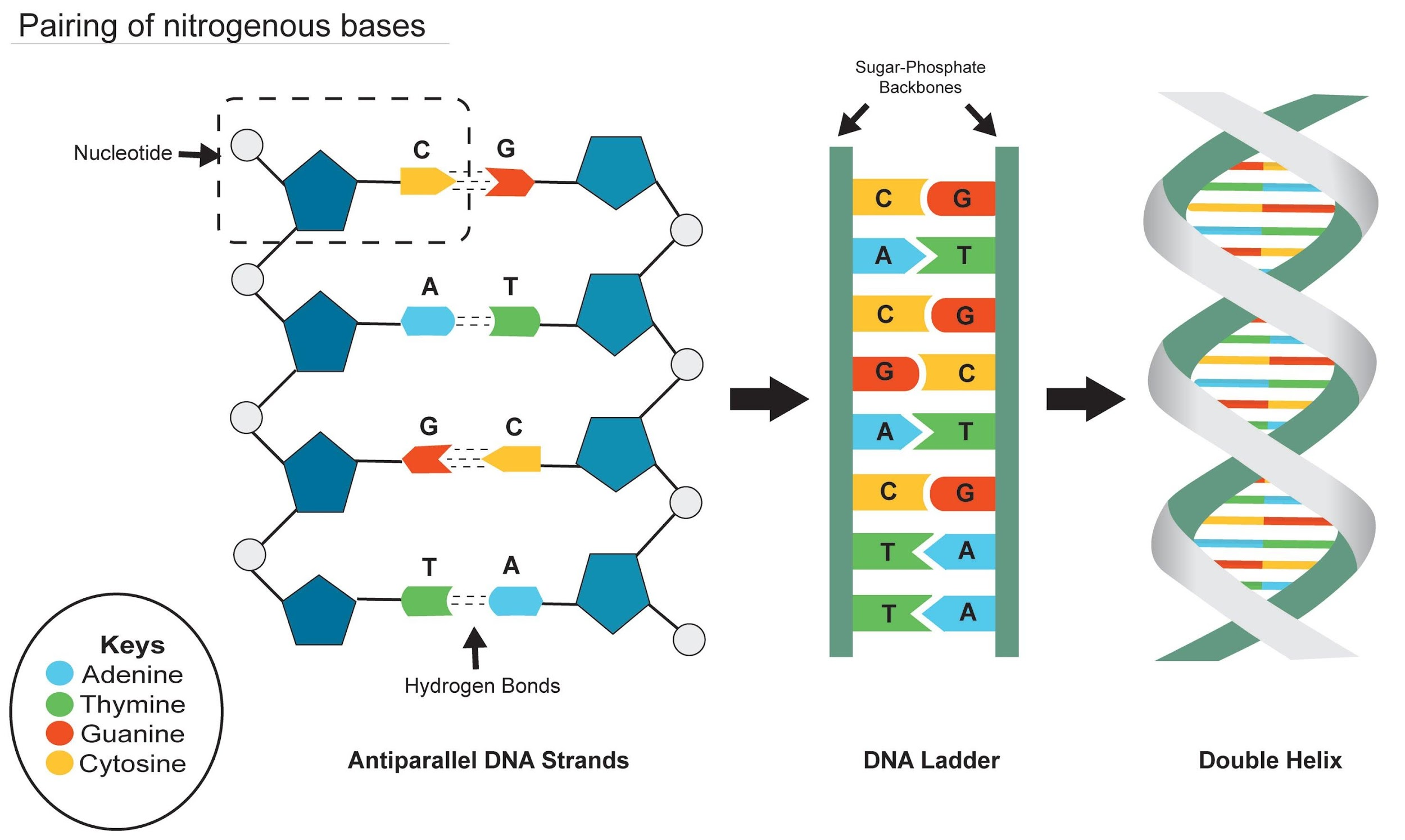
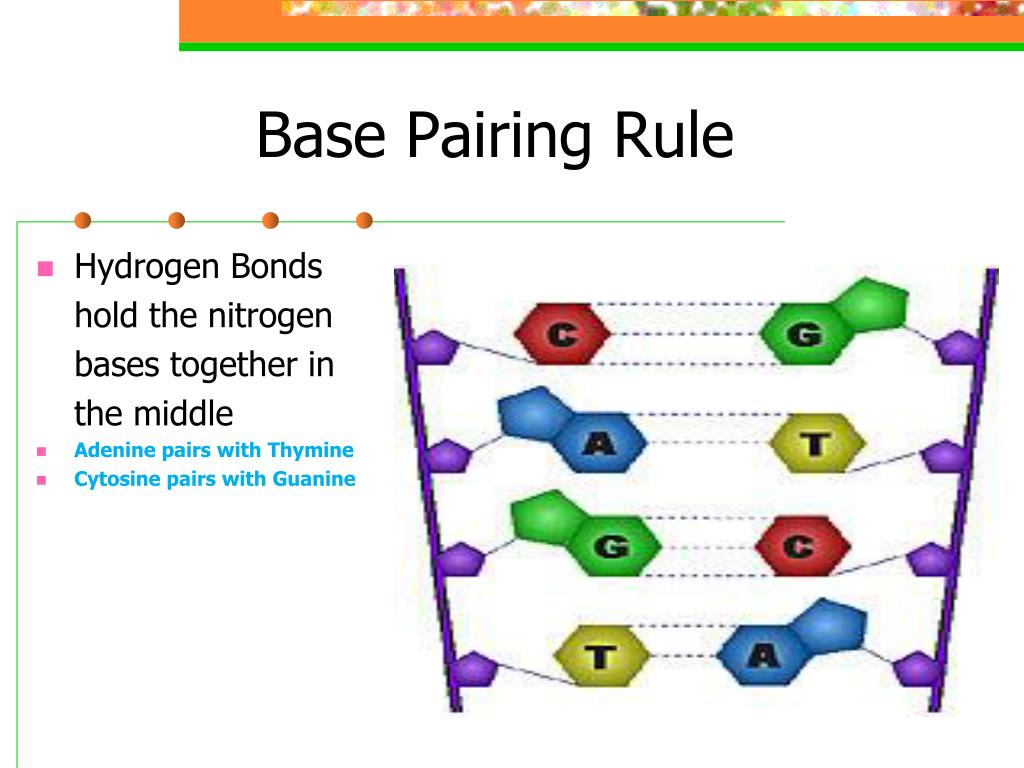
1 Answer. The base-pairing rule describes how the nitrogen bases pair with one another. For DNA replication, the base-pairing rule states that adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine. For transcription from DNA to mRNA, the base-pairing rule states that adenine in DNA always pairs with uracil in mRNA, and.
PPT Microbial PowerPoint Presentation ID6351768
What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? This type of replication is called semi-conservative replication. Considering the meaning of these words (semi—half; conserve—to keep), explain why DNA replication is called semi-conservative.
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology
DNA polymerase needs an "anchor" to start adding nucleotides: a short sequence of DNA or RNA that is complementary to the template strand will work to provide a free 3′ end. This sequence is called a primer (Figure 4). How does DNA polymerase know in what order to add nucleotides? Specific base pairing in DNA is the key to copying the DNA.

How Do Nucleotides Join Together? A Level Biology Phosphodiester
DNA Replication. When the cell enters S (synthesis) phase in the cell cycle, all the chromosomal DNA must be replicated. DNA polymerases synthesize new strands by adding nucleotides to the 3'-OH group present on the previous nucleotide using the separated single strands of DNA as templates. This process generates two new double-stranded molecules, called sister chromatids, from one double helix.

The Structure of DNA Mooramo
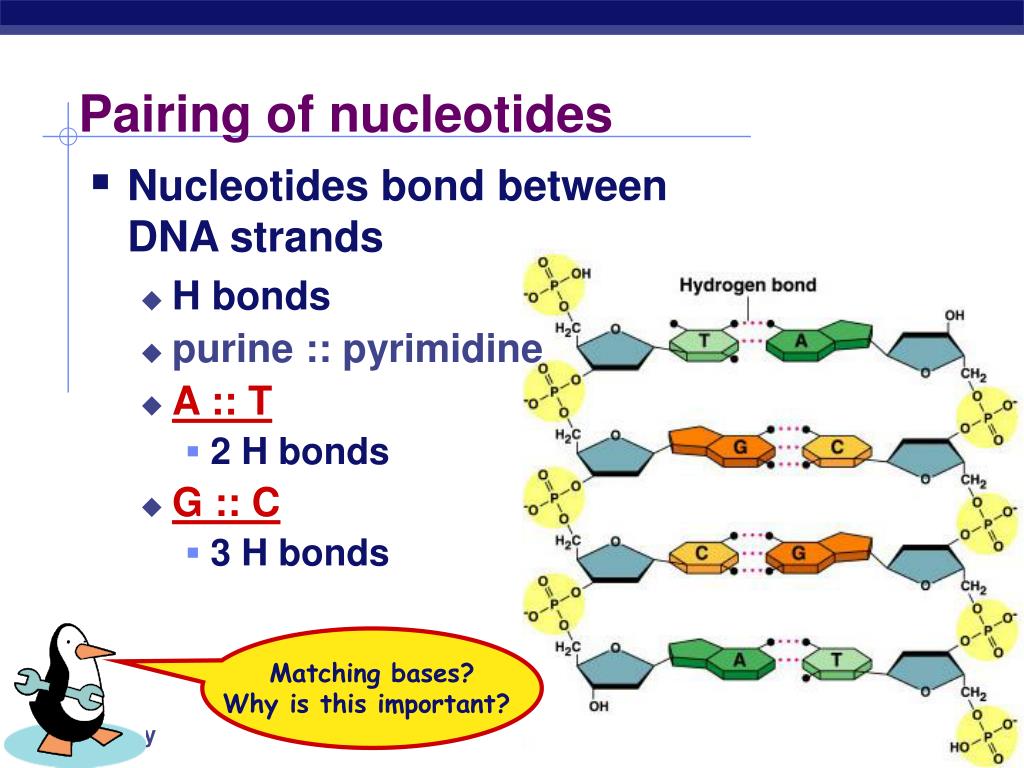
4. Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form. What type of biological molecule is DNA helicase? Enzyme (protein) What it the role of DNA helicase in the replication of DNA? Separates the two strands. What rule is used to join free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? The base pair rule C always connect to G, and A always connects to T.
Label The Diagram Of Dna Nucleotide And Basis
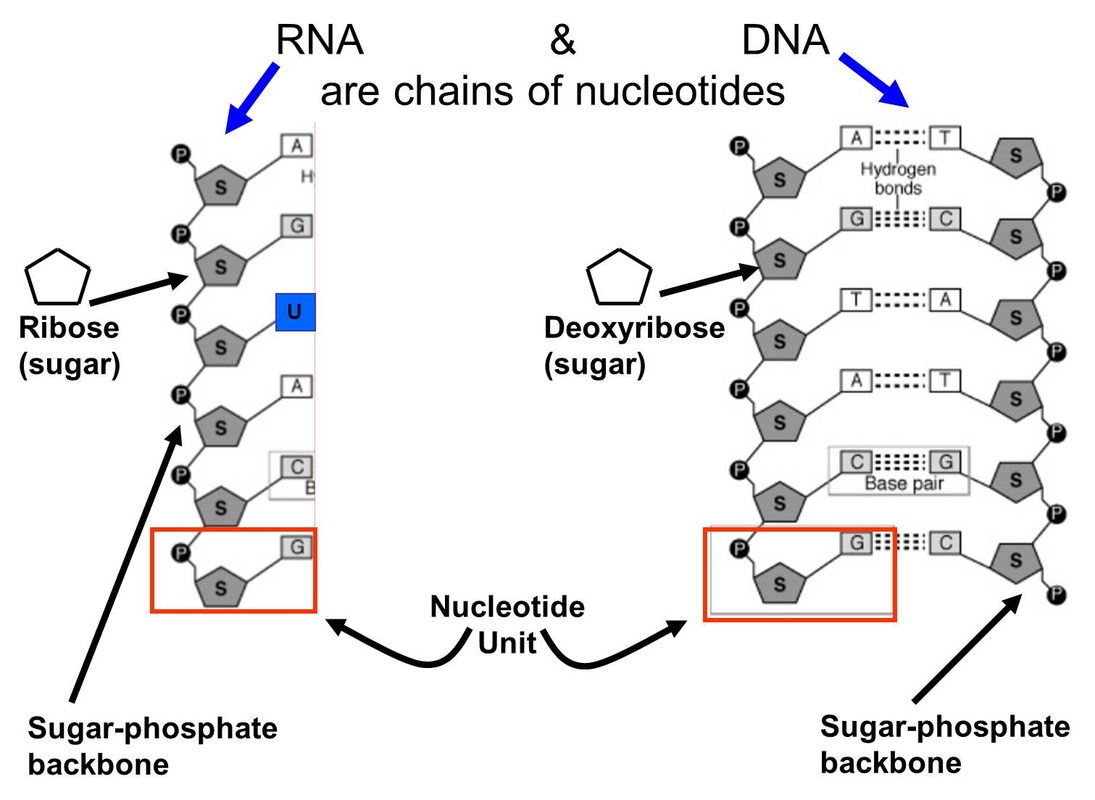
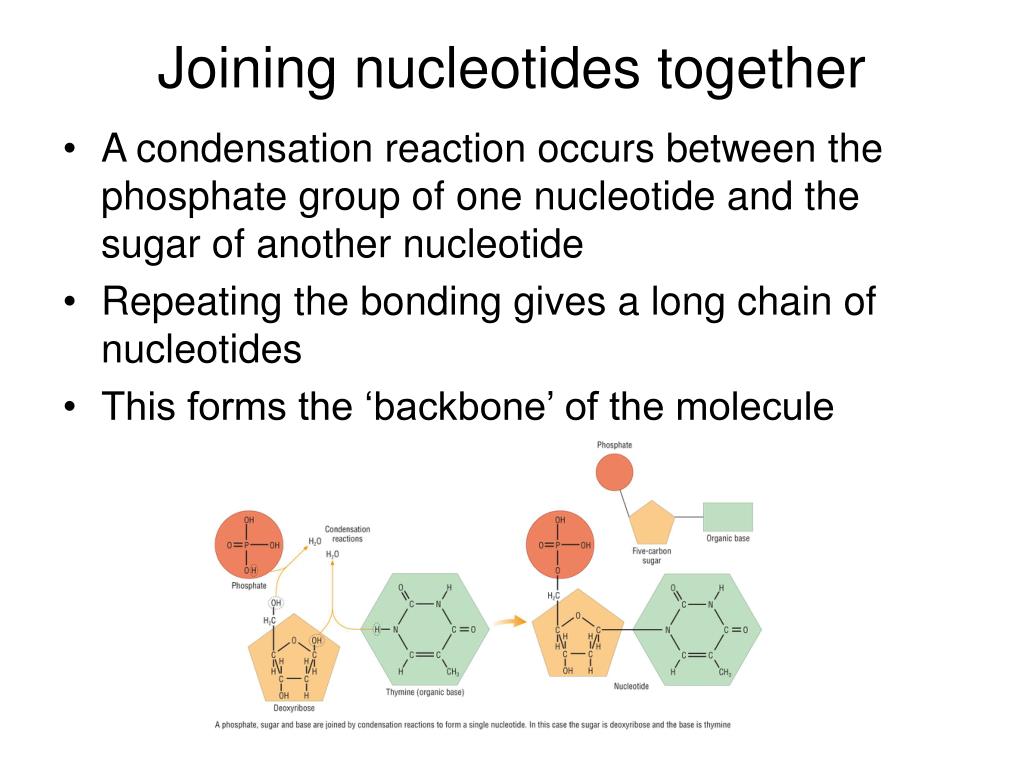
The word "polymerase" is used to describe an enzyme that binds individual small units (nucleotides, in the case of DNA) together to form a long, repeating chain or polymer (a DNA strand). As we have learned, a molecule of DNA is a polymer made of multiple individual units called nucleotides.

Structure and Function of DNA Microbiology
Free DNA nucleotides with extra phosphates pair up with the exposed bases. Neighbouring DNA nucleotides' phosphate and sugars are joined with the help of DNA polymerase. SO, two new DNA are formed each containing a strand from the old DNA. This video provides a brief summary of this process using the DNA Workshop activity from PBS.
DNA Base Pairs — Overview & Structure Expii
What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? 14. This type of replication is called semi-conservative replication. Considering the meaning of these words (semi—half; conserve—to keep), explain why DNA replication is called semi-conservative.
Adenine And Thymine Structure
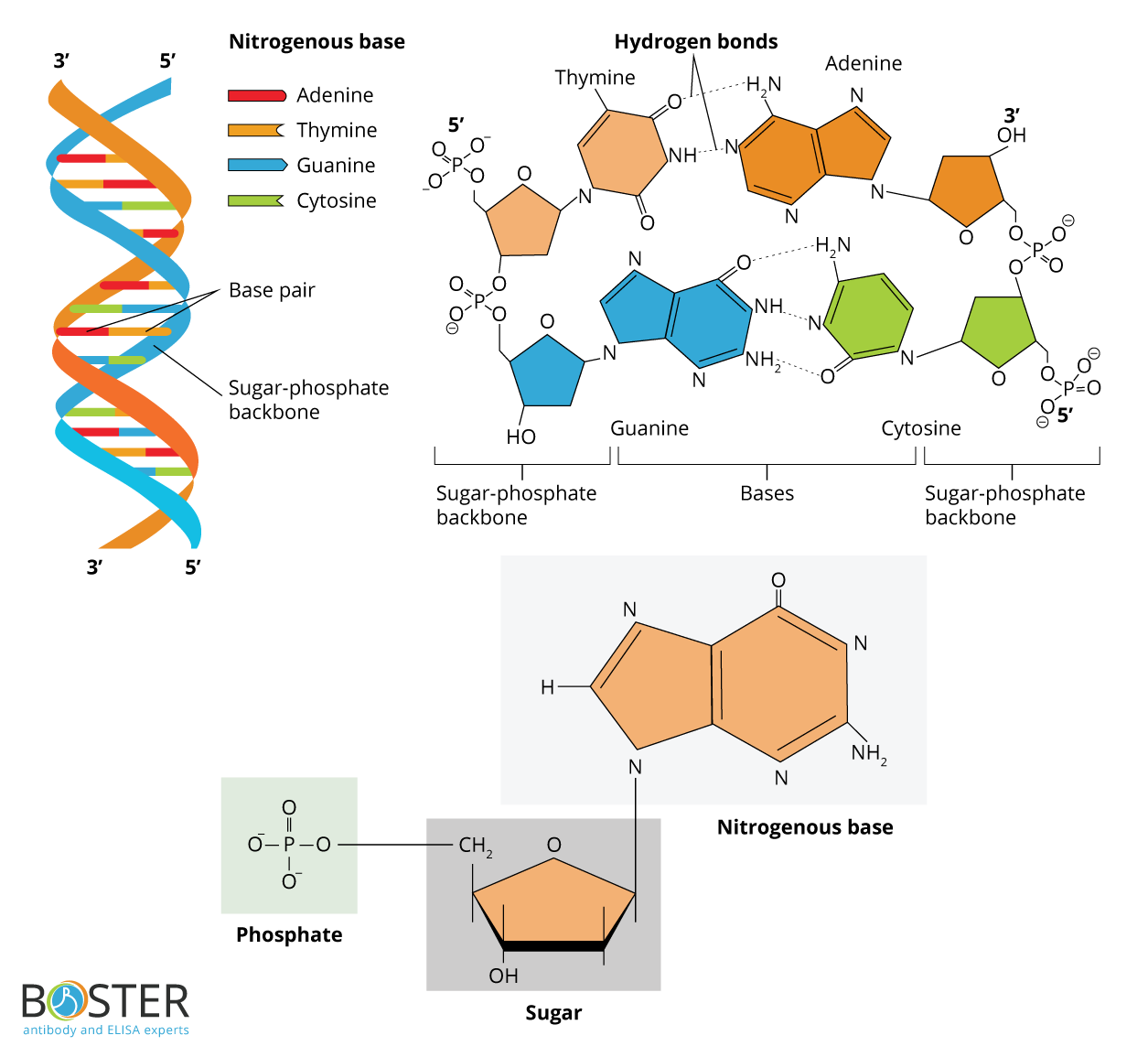
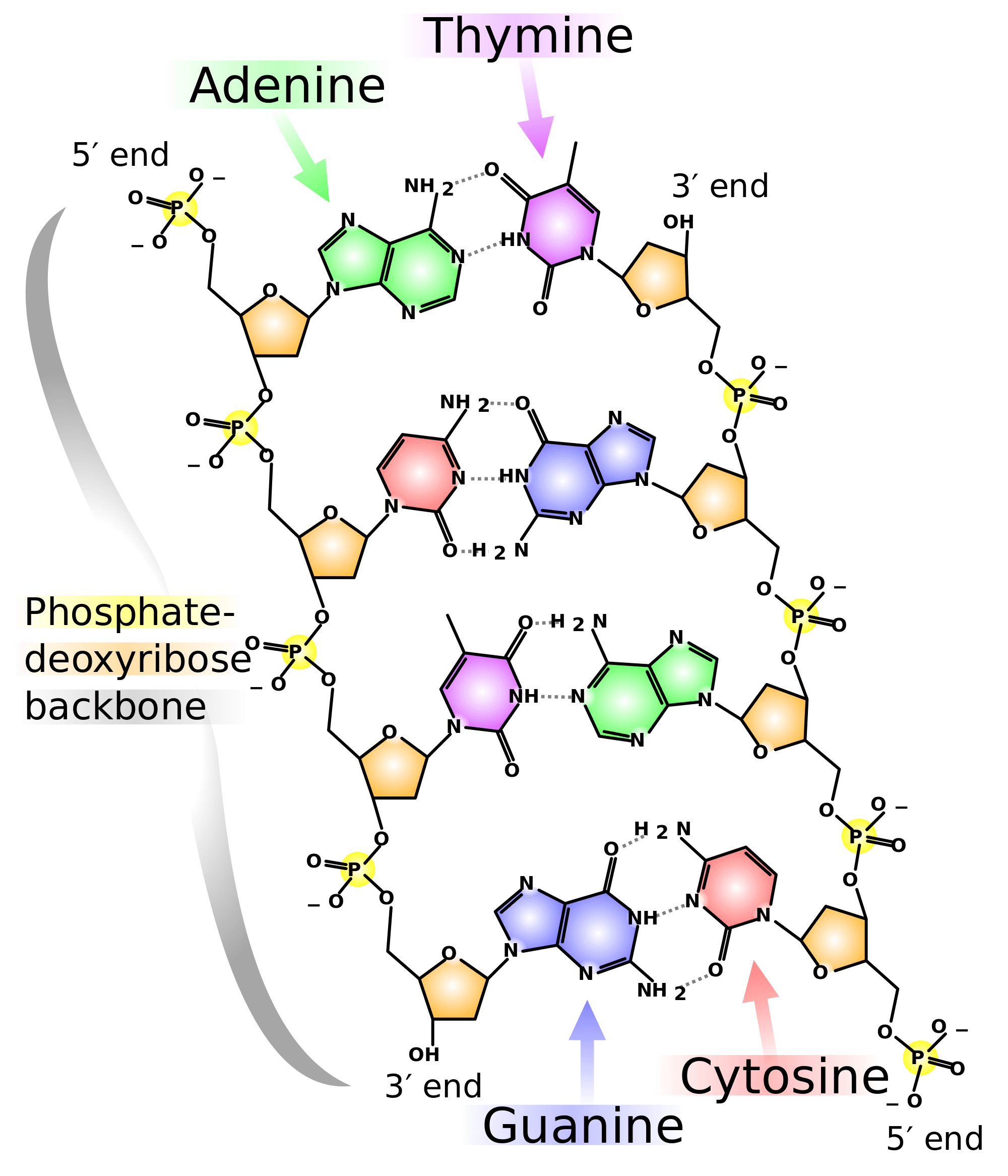
Specific base pairing in DNA is the key to copying the DNA: if you know the sequence of one strand, you can use base pairing rules to build the other strand. Bases form pairs (base pairs) in a very specific way. Figure 8 shows how A (adenine) pairs with T (thymine) and G (guanine) pairs with C (cytosine).

Explain the structure of DNA and RNA nucleotides.
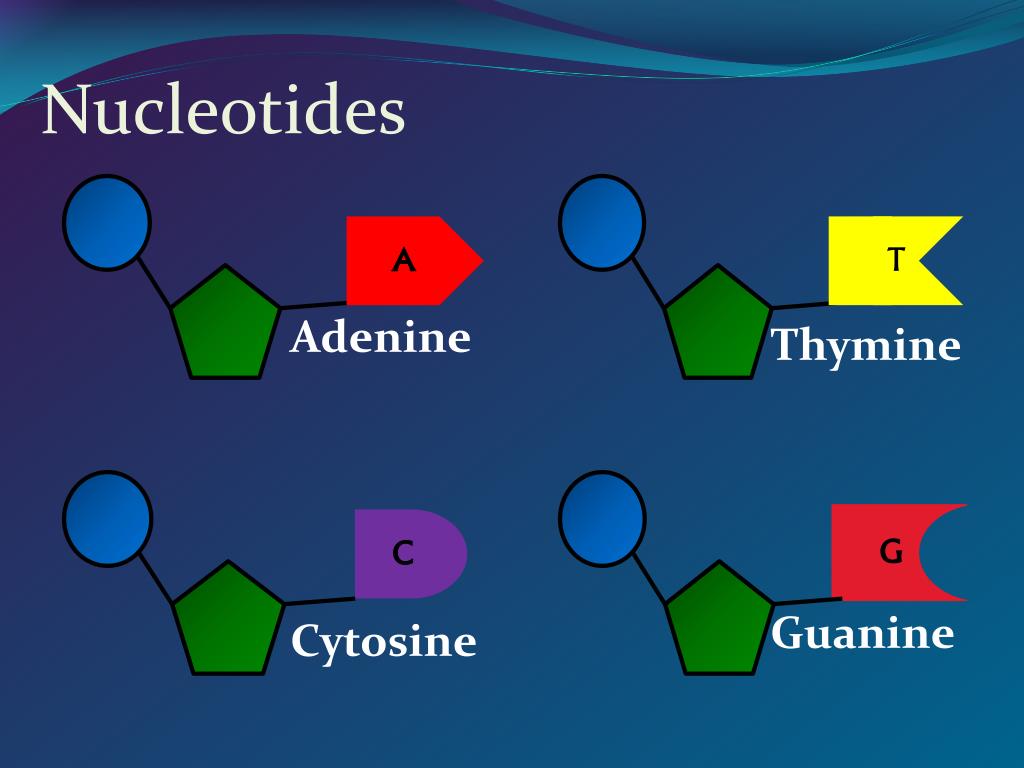
DNA Nucleotides. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Nucleotides that compose DNA are called deoxyribonucleotides. The three components of a deoxyribonucleotide are a five-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, a nitrogen-containing ring structure that is responsible for complementary base pairing between nucleic acid strands (Figure.
PPT DNA Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID144019
What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? Complementary base pair rule.. 1. hydrogen bonds between nucleotids break 2.strands of dna separate 3. free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the loose strands of DNA 4. hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form. About us. About Quizlet;

Nucleotides and Bases Generation
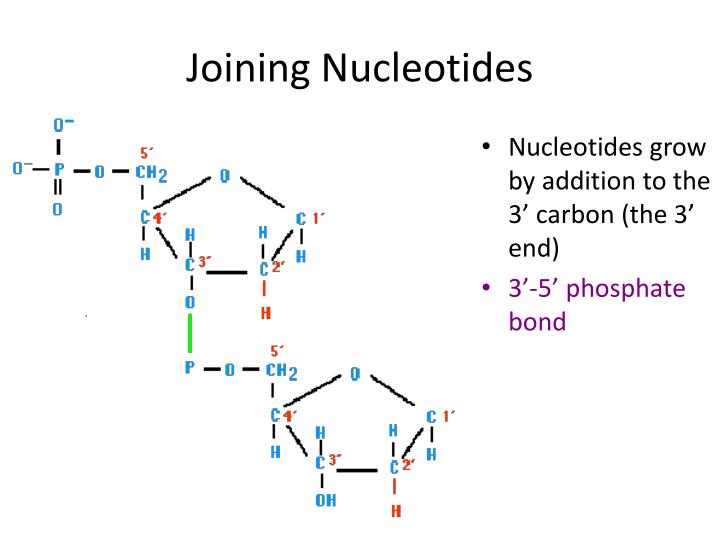
An adenine nucleotide is joined to a cytosine nucleotide. The phosphodiester bond will always link the 5-carbon of one deoxyribose (or ribose in RNA) to the 3-carbon of the next sugar. This also means that on one end of a chain of linked nucleotides, there will be a free 5' phosphate (-PO 4) group, and on the other end, a free 3' hydroxyl.
PPT Nucleotides PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID672807
Free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the loose strands of DNA 4. Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form.. What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? A (Adenine) pairs with T (Thymine) and C (Cytosine) pairs with G (Guanine)
PPT Nucleic Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5327998
Figure 9.2.1 9.2. 1: The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of bases in the other strand. Because of the complementarity of the two strands, having one strand means that it is possible to recreate the other strand. This model for replication suggests that.

What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? Complementary base pair rule.. 1. hydrogen bonds between nucleotids break 2.strands of dna separate 3. free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the loose strands of DNA 4. hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form. About us. About Quizlet;
PPT DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free
Free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the loose strands of DNA 4. Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form.. What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? complementary base pairing. Why is DNA replication called semiconservative? because the replicated double helix consists of one old strand.