CIE A Level Biology复习笔记5.1.1 Chromosome Structure翰林国际教育
Figure 13.1C. 1 13.1 C. 1: A human karyotype: This karyotype is of a male human. Notice that homologous chromosomes are the same size, and have the same centromere positions and banding patterns. A human female would have an XX chromosome pair instead of the XY pair shown.

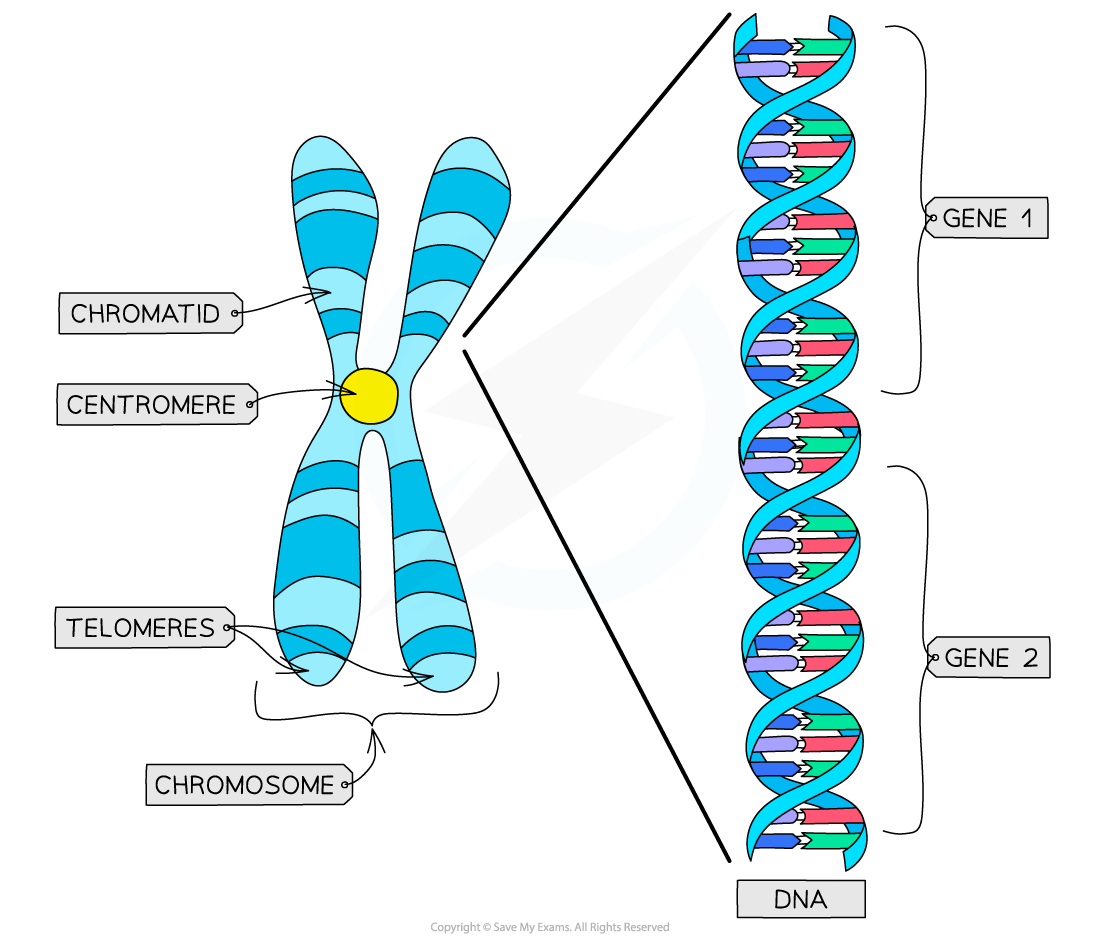
Chromosome Structure
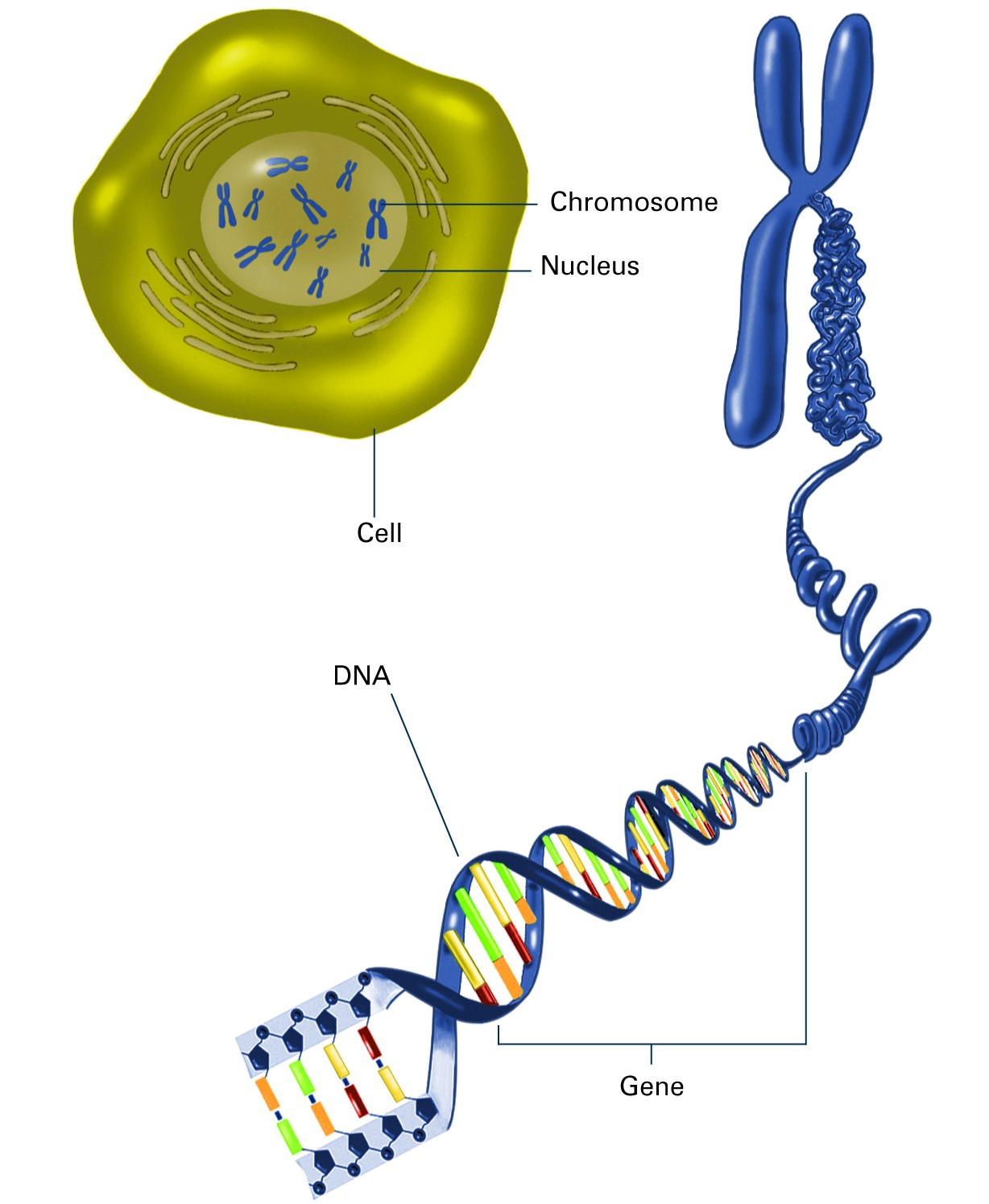
A diagram shows a cell with six X shaped chromosomes in its nucleus. Extending from one of the chromosomes is a stretch of a DNA molecule.. A section of the DNA molecule is labeled as a gene. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell. Each chromosome is made up of a single DNA molecule that contains many genes. Image created with.
Labeled Chromosome
During cell division, it is essential that DNA remains intact and evenly distributed among cells. Chromosomes are a key part of the process that ensures DNA is accurately copied and distributed in the vast majority of cell divisions. Still, mistakes do occur on rare occasions. Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes in new cells may.

Karyotype, karyotype test & analysis, normal karyotype & abnormal karyotype
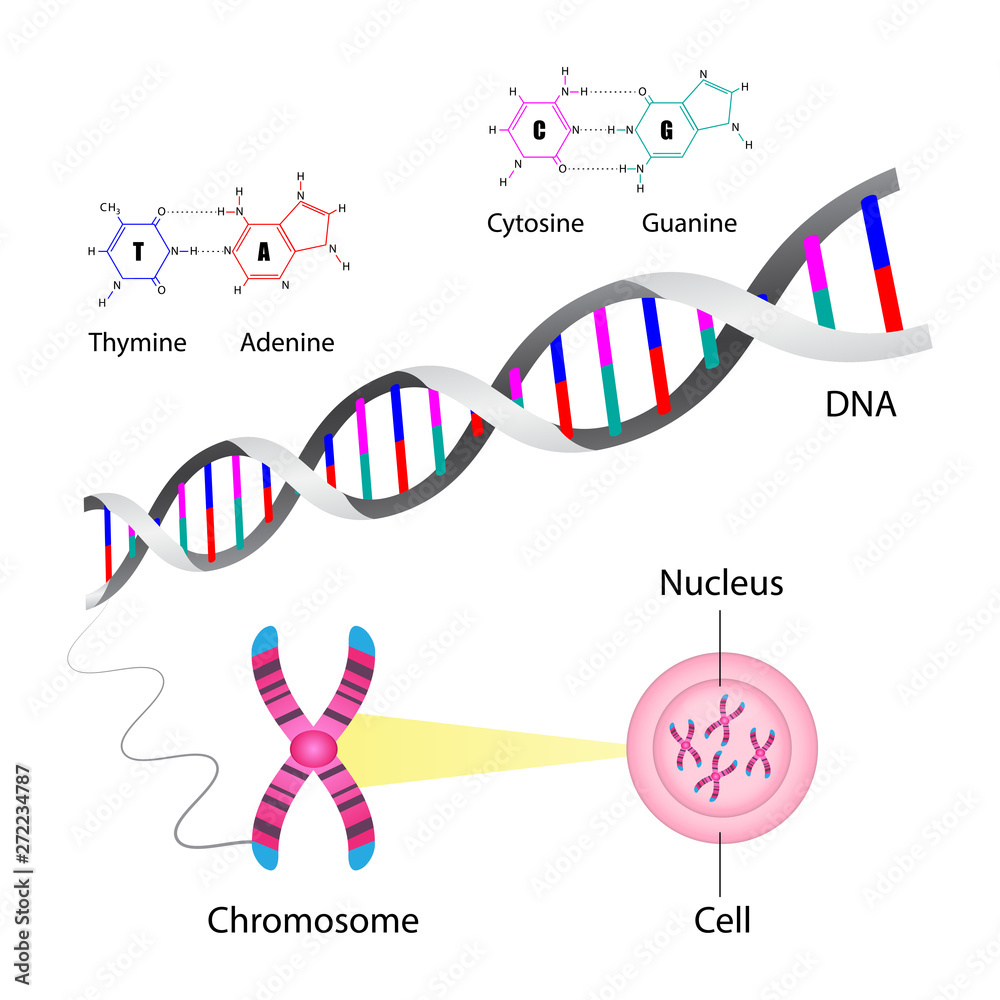
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Structure and types of the eukaryotic chromosomes WikiLectures
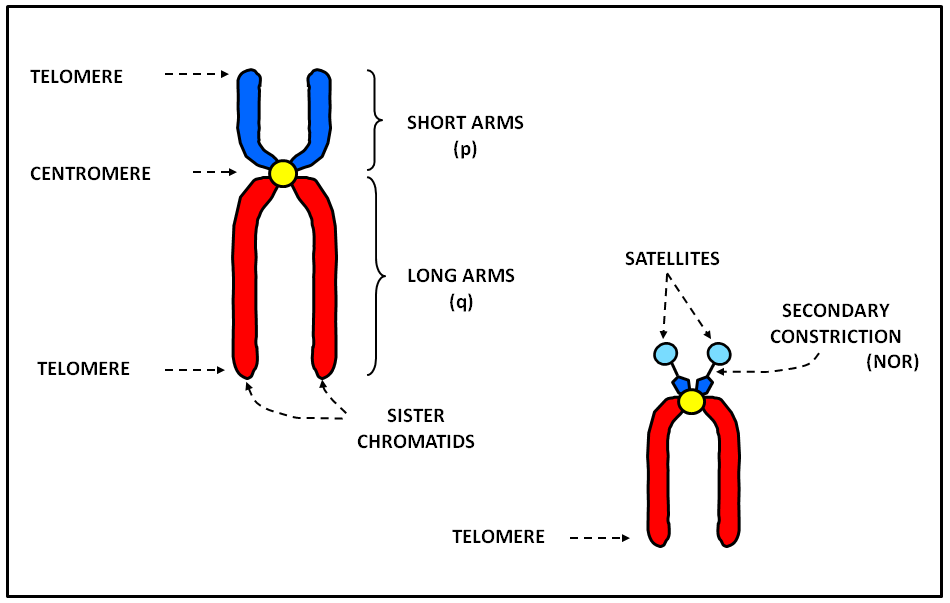
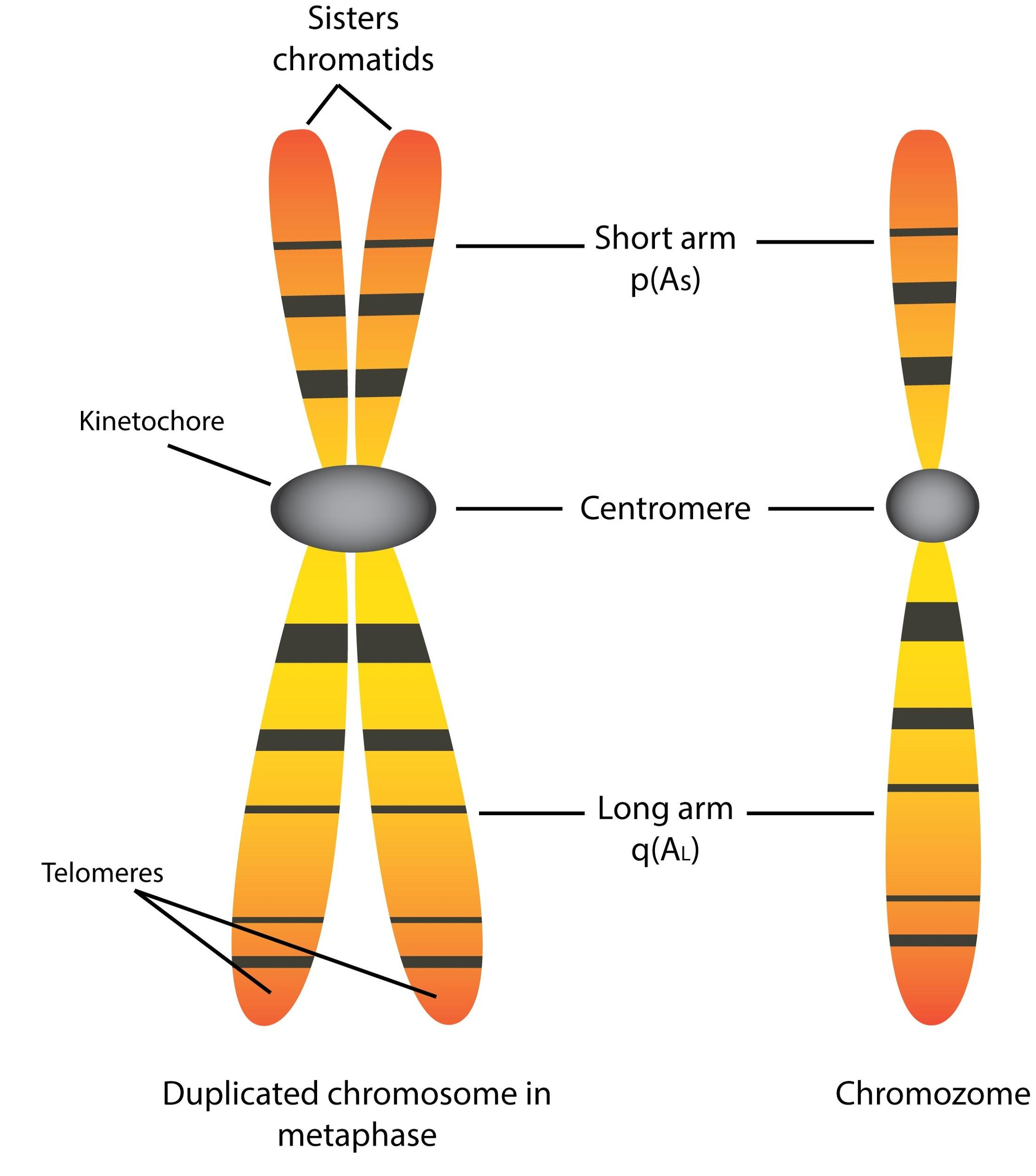
Figure 1 shows an idiogram for chromosome 12, a medium-sized chromosome with one long and one short arm. The position of the centromere, which separates the p and q arms, is shown by the hatched area.
.PNG)
Cell Reproduction. Mitosis and Binary Fission Presentation Biology
Chromosome number. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one homologous.
Things We Don't Know The Secrets of Ageing
chromosome, the microscopic threadlike part of the cell that carries hereditary information in the form of genes. A defining feature of any chromosome is its compactness. For instance, the 46 chromosomes found in human cells have a combined length of 200 nm (1 nm = 10 − 9 metre); if the chromosomes were to be unraveled, the genetic material.

How to make enhanced male sperm
During mitosis, chromosomes become attached to the structure known as the mitotic spindle.In the late 1800s, Theodor Boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his.
Chromatid is(a) One half of chromosome(b) Haploid chromosome(c
Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.. This means that the HBB gene lies on the short arm (p) of chromosome 11 and is found at the band labeled 15.4. With the advent of new techniques in DNA analysis, we are.

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts.

Chromosomes Introduction, Structure & Types A Level Biology Notes
During metaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the metaphase plate—roughly in the midline of the cell, with the kinetochores facing opposite poles. Each homologous pair is oriented randomly at the equator. For example, if the two homologous members of chromosome 1 are labeled a and b, then the chromosomes could line up a-b or.

[Solved] Number of chromosomes in human cell is
Chromosome Structure Labeling. Chromatid Chromosomes DNA Centromere Cell_Membrane Nucleus. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Students label a simple diagram of a chromosome showing the centromere, chromatid, DNA, and the location of the chromosome within the nucleus of.
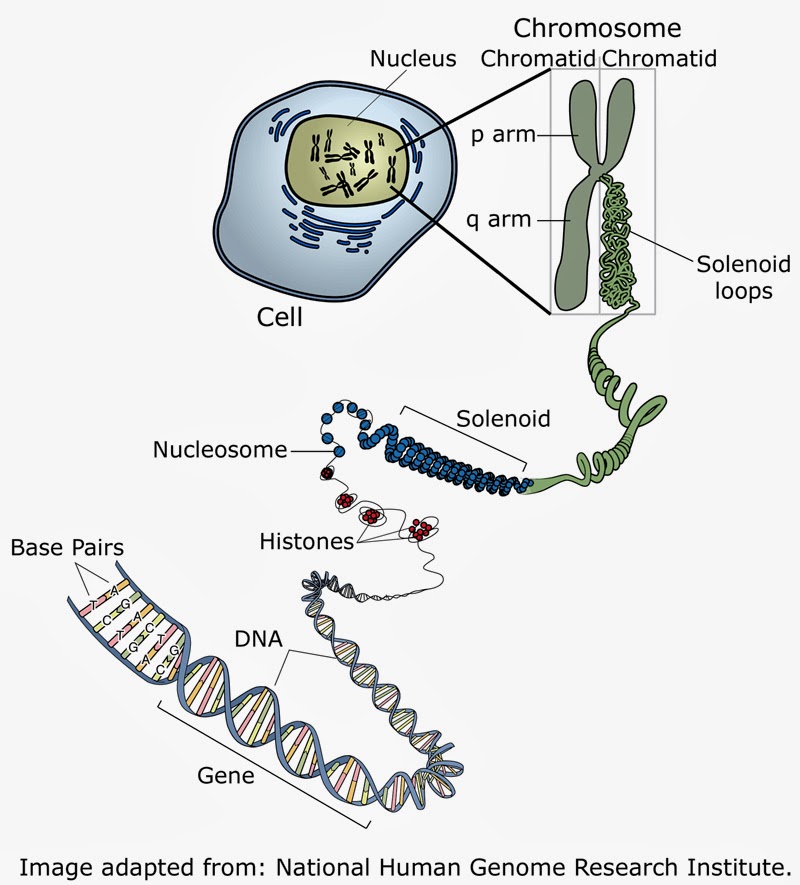
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure. 1. Eukaryotic chromosomes are found in the cell's nucleus. The principal feature that distinguishes a eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cell is the presence of a membrane-bound nucleus. This nucleus is the "control center" of the cell that stores all the cell's genetic information, or DNA.

Chromosome structure Chromosome, Chromosome structure, Structural biology
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a complete diploid set: a new genome.

What are homologous chromosomes? Biology Stack Exchange
Most of what researchers know about chromosomes was learned by observing chromosomes during cell division. Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, or "arms." The short arm of the chromosome is labeled the "p arm." The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the "q.
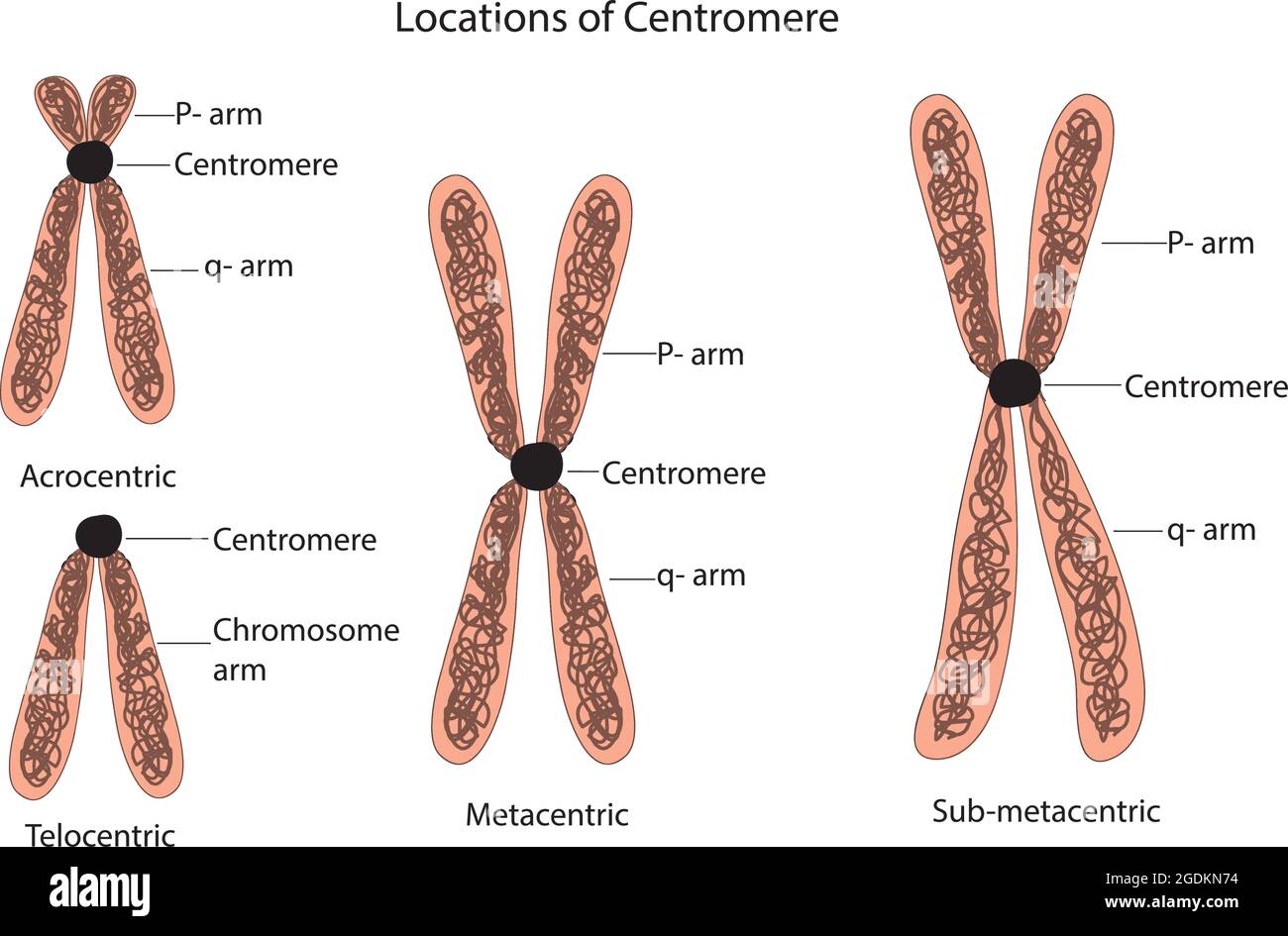
classification of chromosomes centromere, chromosome classifications
Moreover, the chromosome number is constant for a particular species. Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged as 23 pairs. Here, 22 pairs are autosomes or body chromosomes and the 23rd pair is allosome or sex chromosome. Let us learn more about the structure of the chromosome with the help of a diagram. Diagram Showing Chromosome